Arduino Communication Protocols
ABB PowerOne Aurora inverter communication protocol: Arduino ABB PowerOne Aurora inverter communication protocol, esp8266 and esp32 Library. ACAN: A Teensy 3.1 / 3.2, 3.5, 3.6 CAN driver. ACAN2515: Driver for MCP2515 CAN Controller: ACAN2515Tiny: Driver for MCP2515 CAN Controller: ACAN2517: Driver for the MCP2517FD and the MCP2518FD CAN. TCP/IP model: The Internet protocol suite is the conceptual model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP because the foundational protocols in the of it are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP).
- Arduino Tutorial
- Arduino Function Libraries
- Arduino Advanced
- Arduino Projects
- Arduino Sensors
- Motor Control
- Arduino And Sound
There are many types of protocols that are used in transferring data between two devices, but all these protocols are based on either Parallel Communication or Serial Communication. Select the Next Set of Arduino Projects You Want to Learn in Electronicshub: Arduino Projects ». $2 for 5PCBs (Any solder mask colour): In this video I show you more or less how i2c, UART and SPI serial communications work with a few e. In this tutorial, we’ll discuss what the I2C communication protocol is, how it works, and how to use it on the Arduino. To demonstrate, we’re going to build a project that uses I2C communication to exchange data between two Arduino microcontrollers. I2C is an acronym for Inter-Integrated Circuit.
- Arduino Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
Hundreds of communication protocols have been defined to achieve this data exchange. Each protocol can be categorized into one of the two categories: parallel or serial.
Parallel Communication
Parallel connection between the Arduino and peripherals via input/output ports is the ideal solution for shorter distances up to several meters. However, in other cases when it is necessary to establish communication between two devices for longer distances it is not possible to use parallel connection. Parallel interfaces transfer multiple bits at the same time. They usually require buses of data - transmitting across eight, sixteen, or more wires. Data is transferred in huge, crashing waves of 1’s and 0’s.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Parallel Communication
Parallel communication certainly has its advantages. It is faster than serial, straightforward, and relatively easy to implement. However, it requires many input/output (I/O) ports and lines. If you have ever had to move a project from a basic Arduino Uno to a Mega, you know that the I/O lines on a microprocessor can be precious and few. Therefore, we prefer serial communication, sacrificing potential speed for pin real estate.
Serial Communication Modules
Today, most Arduino boards are built with several different systems for serial communication as standard equipment.
Which of these systems are used depends on the following factors −

- How many devices the microcontroller has to exchange data with?
- How fast the data exchange has to be?
- What is the distance between these devices?
- Is it necessary to send and receive data simultaneously?
One of the most important things concerning serial communication is the Protocol, which should be strictly observed. It is a set of rules, which must be applied such that the devices can correctly interpret data they mutually exchange. Fortunately, Arduino automatically takes care of this, so that the work of the programmer/user is reduced to simple write (data to be sent) and read (received data).

Types of Serial Communications
Serial communication can be further classified as −
Synchronous − Devices that are synchronized use the same clock and their timing is in synchronization with each other.
Asynchronous − Devices that are asynchronous have their own clocks and are triggered by the output of the previous state.
It is easy to find out if a device is synchronous or not. If the same clock is given to all the connected devices, then they are synchronous. If there is no clock line, it is asynchronous.
For example, UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) module is asynchronous.
The asynchronous serial protocol has a number of built-in rules. These rules are nothing but mechanisms that help ensure robust and error-free data transfers. These mechanisms, which we get for eschewing the external clock signal, are −
- Synchronization bits
- Data bits
- Parity bits
- Baud rate

Synchronization Bits
The synchronization bits are two or three special bits transferred with each packet of data. They are the start bit and the stop bit(s). True to their name, these bits mark the beginning and the end of a packet respectively.
There is always only one start bit, but the number of stop bits is configurable to either one or two (though it is normally left at one).
The start bit is always indicated by an idle data line going from 1 to 0, while the stop bit(s) will transition back to the idle state by holding the line at 1.
Data Bits
The amount of data in each packet can be set to any size from 5 to 9 bits. Certainly, the standard data size is your basic 8-bit byte, but other sizes have their uses. A 7-bit data packet can be more efficient than 8, especially if you are just transferring 7-bit ASCII characters.
Parity Bits
The user can select whether there should be a parity bit or not, and if yes, whether the parity should be odd or even. The parity bit is 0 if the number of 1’s among the data bits is even. Odd parity is just the opposite.
Baud Rate
The term baud rate is used to denote the number of bits transferred per second [bps]. Note that it refers to bits, not bytes. It is usually required by the protocol that each byte is transferred along with several control bits. It means that one byte in serial data stream may consist of 11 bits. For example, if the baud rate is 300 bps then maximum 37 and minimum 27 bytes may be transferred per second.
Arduino UART
The following code will make Arduino send hello world when it starts up.
After the Arduino sketch has been uploaded to Arduino, open the Serial monitor at the top right section of Arduino IDE.
Type anything into the top box of the Serial Monitor and press send or enter on your keyboard. This will send a series of bytes to the Arduino.
The following code returns whatever it receives as an input.
The following code will make Arduino deliver output depending on the input provided.
Notice that Serial.print and Serial.println will send back the actual ASCII code, whereas Serial.write will send back the actual text. See ASCII codes for more information.
When it sees you, it won't stop following!
Face Tracking Camera
Project tutorial by Little_french_kev
- 27,540 views
- 21 comments
- 97 respects
Serial Communication between ESP2866-12 (NODE-MCU) and Arduino to increase the number of analog pins as my primary work.
Serial Communication between NodeMCU and Arduino
Project showcase by Pawan Kumar
- 96,510 views
- 12 comments
- 35 respects
This device runs a desired length and quantity of wires and cuts each length.
Simple Wire Length Cutting Tool
Project in progress by 30percent
- 11,510 views
- 15 comments
- 66 respects
Use a Bluetooth module to replace a traditional wired connection for transmitting serial data.
View Serial Monitor Over Bluetooth
by millerman4487
- 29,495 views
- 12 comments
- 38 respects
Three ways to use Arduino as a USB to TTL converter. Helpful one!
Ways to Use Arduino as USB to TTL Converter
by Patel Darshil
- 64,469 views
- 10 comments
- 14 respects
The Arduino is simple, cheap and power efficient but has limitations. Sometimes, you may want to have more than one access your I2C bus.
Arduino I2C Multi-Master Approach - Why and How
by Chip McClelland
- 21,401 views
- 10 comments
- 15 respects
If you've ever wanted to connect devices with just 3 pins, this is the perfect project for you!
Using I2C Communication Protocol to Connect 6 Arduino Megas
Project showcase by Sherwin Chiu
- 7,938 views
- 11 comments
- 29 respects
This article will show how to communicate between Arduino and Visual Studio through COM (UART) port.
Arduino - Serial Communication Visual Studio
Project tutorial by engineer2you
- 33,605 views
- 6 comments
- 28 respects
With the coming .NET Core 3.0, cross-platform serial port is available. Let's have a try on RPi Raspbian.
Serial Communication with .NET Core 3.0 on RPi Linux
by Leon Song
- 30,748 views
- 5 comments
- 16 respects
This project will show you how to use temperature and hmidity (DHT11 and DHT22) sensors with an Arduino card.
How to Use Temperature and Humidity (DHT) Sensors
by MisterBotBreak
- 55,476 views
- 4 comments
- 35 respects
Bring the versatility of the Arduino Uno to the powerful world of IoT with the Onion Omega board. Make any Arduino project IoT compatible.
Interfacing the Onion Omega2 and Arduino Uno via UART
by Shervin Oloumi
- 6,690 views
- 6 comments
- 21 respects
This is a step-by-step tutorial on how to use the RAK811 LoRA node module and send LoRa packets to a gateway.
Getting Started With the RAK811 LoRa Node
by Naresh krish
- 22,348 views
- 4 comments
- 16 respects
Arduino and Python-based project that will help us read the sensor values and plot it on Python.
Arduino Real-Time Plotting with Python
by Asim Zulfiqar and High Voltages
- 22,523 views
- 3 comments
- 18 respects
I made a tool to program the Arduino Pro Mini without the need to solder pins to attach the USB bus port.
Programming the Arduino Pro Mini without Soldering Pins
Project showcase by Ruben Zilzer
- 4,365 views
- 4 comments
- 28 respects
Arduino and Python-based project that will help us read the sensor values and plot it on MATLAB.
Arduino Real-Time Plotting with MATLAB
Project tutorial by Asim Zulfiqar and High Voltages
- 17,337 views
- 2 comments
- 22 respects
In this project I will guide you on how to make your own Arduino Chameleon using TCS3200 and Arduino Uno.

Arduino Chameleon Using TCS3200
by Manan Thareja
- 2,716 views
- 3 comments
- 3 respects
This project helps you to send strings from computer to your Arduino via serial port.
How to Get String Data from Computer via Serial Port
by Phuong Vo
- 6,619 views
- 2 comments
- 12 respects
Using cheap 433 MHZ RF module to establish communication between my PC and Laptop, but displays information encrypted on text LCD.
Sending Data from PC to Another Using Arduino UNO
Project tutorial by Mohamed Maher
- 5,946 views
- 2 comments
- 14 respects
We implement RS-485 protocol in communication between two Arduinos using MAX485 module.
Modbus (RS-485) Using Arduino
Project showcase by Maurizfa (13216008) / Arthur Jogy (13216037) / Agha Maretha (13216095)
- 19,109 views
- 0 comments
- 5 respects
We implement CAN Bus communication with MCP2515 module to communicate between two Arduino for sending temperature data from DHT
CAN Bus Using Arduino
Arduino Communication Protocols Jobs
Project showcase by Maurizfa (13216008) / Arthur Jogy (13216037) / Agha Maretha (13216095)
- 10,017 views
- 0 comments
- 4 respects
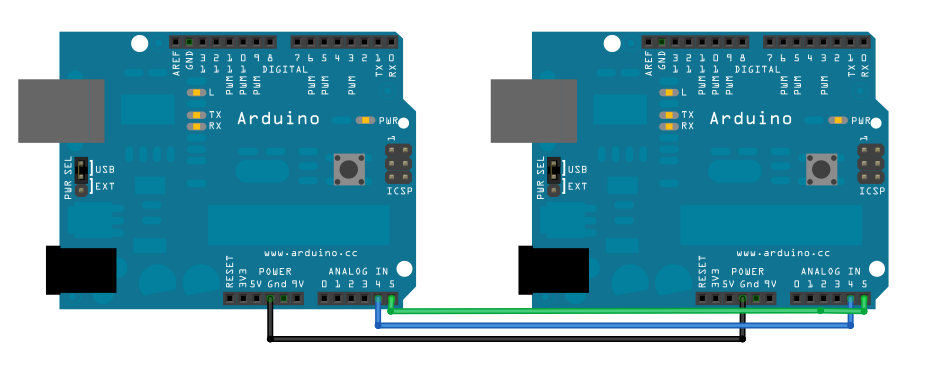
If you want use two Arduino, you can use a simple I/O port to communicate. The point of question is the Ground.
Communication Between Arduino UNO
by Giovanni Gentile
Arduino Communication Protocols Example
- 6,438 views
- 1 comment
- 8 respects
